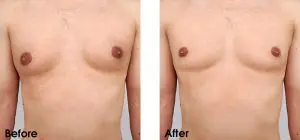
What is this procedure?
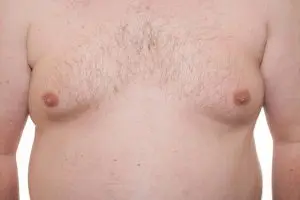
Gynecomastia is swelling of the breast tissue in boys or men, caused by an imbalance of the hormones estrogen and testosterone. Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts, sometimes unevenly. Newborns, boys going through puberty and older men may develop gynecomastia as a result of normal changes in hormone levels, though other causes also exist.
Generally, gynecomastia isn’t a serious problem, but it can be tough to cope with the condition. Men and boys with gynecomastia sometimes have pain in their breasts and may feel embarrassed.
Gynecomastia may go away on its own. If it persists, medication or surgery may help. Gynecomastia is triggered by a decrease in the amount of the hormone testosterone compared with estrogen. The cause of this decrease can be conditions that block the effects of or reduce testosterone or a condition that increases your estrogen level. Several things can upset the hormone balance, including the following
Natural hormone changes
The hormones testosterone and estrogen control the development and maintenance of sex characteristics in both men and women. Testosterone controls male traits, such as muscle mass and body hair. Estrogen controls female traits, including the growth of breasts.
Most people think of estrogen as an exclusively female hormone, but men also produce it — though normally in small quantities. However, male estrogen levels that are too high or are out of balance with testosterone levels can cause gynecomastia.
- Gynecomastia in infants. More than half of male infants are born with enlarged breasts due to the effects of their mother’s estrogen. Generally, the swollen breast tissue goes away within two to three weeks after birth.
- Gynecomastia during puberty. Gynecomastia caused by hormone changes during puberty is relatively common. In most cases, the swollen breast tissue will go away without treatment within six months to two years.
- Gynecomastia in men. The prevalence of gynecomastia peaks again between the ages of 50 and 69. At least 1 in 4 men in this age group are affected.
Gynecomastia results in an increase in breast tissue in males that, when problematic, is readily detectable by other individuals. The increased tissue may be breast glandular tissue, adipose (fatty) in nature, or a combination of the two. This results in significant functional and psychological limitations.
The physical deformation may also be exquisitely painful. As a general rule, the glandular tissue is significantly more painful than the fatty tissue. Situations like gym class may require children or adolescents to remove their shirts in the presence of other students. This can put a boy with gynecomastia in danger not only of embarrassment but also of physical harm.
Most patients have never heard of this condition until the family physician identifies it. The physician may be unaware of the possible causes of the condition and its psychological impact. After initial presentation, boys are frequently advised to ignore the gynecomastia and are told that it will go away.
Fortunately, in most instances, cases of minimal subareolar pubertal-onset gynecomastia do regress as puberty progresses. Individuals with no regression or even progression of the deformity often receive little or no understanding about the shame and humiliation they experience. Coaches, sergeants, physicians, parents, and peers (both boys and girls) can inflict damage out of ignorance, cruelty, or both. The author reports that a parent recently exclaimed during an initial evaluation, “I just don’t understand why ‘he’ has to slouch around all the time.” Postural and clothing modifications to mask the deformity are the norm in these patients from puberty through adulthood.
Who needs this procedure?
Gynecomastia surgery candidates include:
- Men whose condition cannot be corrected through alternative medical treatments
- Healthy individuals who do not have a life-threatening illness or medical conditions that can impair healing
- Nonsmokers and non-drug users
- Men with a positive outlook and specific goals in mind for improving the physical symptoms of gynecomastia
- Men who are physically healthy and of relatively normal weight
- Men who have realistic expectations
- Men whose breast development has stabilized
- Men who are bothered by the feeling that their breasts are too large
Adolescents may benefit from surgery, although secondary procedures may be needed in the future should breast development continue.
What is the advantage of this procedure?
Male breast reduction surgery is the leading treatment for gynecomastia and is exceptionally successful. This procedure may involve excision, liposuction, or a combination of both to address skin laxity as well as excess fat to achieve the desired results. Some patients even pair this procedure with tummy tuck surgery to produce a stronger and tighter core that complements their newly formed chest. Gynecomastia surgery relieves men of the embarrassment caused by having the condition and restores their chest to a more masculine appearance. Undergoing this procedure provides a broader range of benefits for a man than any other aesthetic surgical procedure would.
#1: Boosts Confidence & Self-Esteem
Many men can become depressed as a result of the body insecurities caused by gynecomastia that cannot be easily remedied with lifestyle changes. Creating a firmer, flatter chest aesthetic provides an instant boost of self-esteem for men who suffer from gynecomastia. Having a flatter chest as a result of male breast reduction surgery allows patients to wear more fitted clothing, go shirtless at the beach or pool, and not shy away from social interactions due to low self-esteem.
#2: Enjoy a More Masculine Figure
For most men, being compared to the female form is not a compliment. Unfortunately, many men who have gynecomastia are made to feel as though their body shape is not compatible with their gender. Male breast reduction removes the excess fatty tissue from the chest, giving men the option to show off a flatter chest and a more sculpted physique. Men who opt for male breast reduction surgery can enjoy their new, masculine chest and rid themselves of the insecurities they once struggled with.
#3: Eases Physical Activity
Having a larger chest with more fatty tissue makes physical activity uncomfortable, which is something many women can relate to. Exercises, such as running and jumping, become more difficult and embarrassing if you are aware of the movements of your chest. While women can choose from a variety of special athletic bras that help hold their breasts down and prevent painful movement during exercise, men do not have the same options. Reducing the size of the chest allows male patients to feel comfortable engaging in physical activity again, which helps motivate them to stay fit and maintain their stronger, firmer figure.
#4: Improves Posture
Having a more substantial chest can have a dramatic effect on one’s posture, causing the upper spine to become rounder and disfigured. Over time, this can lead to a permanent hump and chronic spinal pain. Another consequence of poor posture is compromised core strength and a withdrawn or reserved appearance. Sometimes, it is not the weight of the breasts that causes slouching, but men with gynecomastia may hunch their backs to hide their chest. With a smaller chest, patients can stand straighter and taller, exuding confidence and approachability.
#5: Free Your Mind
The mind can flood itself with negative thoughts, especially when someone is self-conscious about their body. Men with gynecomastia may experience intense levels of anxiety throughout their day when considering what to wear, how to hide their chest, and whether anyone has noticed their breasts. Men who opt for male breast reduction can alleviate these worries and free their minds of constant uneasiness so that they can enjoy their lives and social interactions. Most male breast reduction patients report experiencing a heightened quality of life and emotional relief after their treatment.
Are there non-surgical treatments?
Treatment of gynecomastia is not always necessary since transient gynecomastia, such as occurs during puberty, generally resolves on its own without treatment within three years. If medications are the cause of gynecomastia, stopping the offending drug can be effective in reducing gynecomastia. Moreover, treatments for gynecomastia have not been extensively studied, so data showing their effectiveness are limited. No drugs have yet been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of gynecomastia. In general, two types of medications have shown promise for the management of gynecomastia:
Testosterone replacement: This therapy has been effective in older men with low levels of testosterone, but it was not proved to be effective for men who have normal levels of the male hormone.
SERMs: The selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) tamoxifen(Soltamox) and raloxifene (Evista) can help reduce the amount of breast tissue, although they are not able to entirely eliminate the problem. These medications are most often used for severe or painful gynecomastia.
What is the surgical treatment like local or sedation?
Anesthesia Medications are administered for your comfort during the surgical procedures. The options include intravenous sedation and general anesthesia. Your doctor will recommend the best option for you.
How long does it take?
Liposuction technique
In cases where gynecomastia is primarily the result of excess fatty tissue, liposuction techniques alone may be used. This requires insertion of a cannula, a thin hollow tube, through several small incisions. The cannula is moved back and forth in a controlled motion to loosen the excess fat, which is then removed from the body by vacuum suction. There are various liposuction techniques that may be used; the technique most appropriate in your case will be defined prior to your procedure.
Excision technique
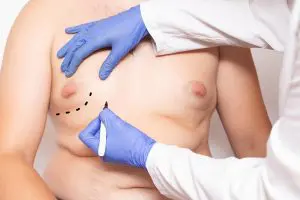
Excision techniques are recommended where glandular breast tissue or excess skin must be removed to correct gynecomastia. Excision also is necessary if the areola will be reduced or the nipple will be repositioned to a more natural male contour. Incision patterns vary depending on the specific conditions and surgical preference. Sometimes gynecomastia is treated with both liposuction and excision.
How long has it been around?
Gynecomastia is derived from the Greek terms gynec (feminine) and mastos (breast). The literal translation, male breasts, relates to any condition that results in excessive development of breast tissue in males. Males may rarely develop breast cancer, but this is often associated with testicular atrophy.
Male breast volume is composed of a combination of ductal and stromal tissue, commonly referred to as glandular tissue, and an increase in adipocytes, typically referred to as fatty tissue. Excess skin resulting in significant ptosis of the breast may be present in patients with severe gynecomastia.
Galen introduced the term gynecomastia in the second century AD. He defined gynecomastia as an unnatural increase in the breast fat of males. Although Galen was aware that glandular enlargement of the male breast occurred as a separate entity, he did not consider this gynecomastia.
The first recorded description of a reduction mammaplasty was by Paulas of Aegina in the seventh century AD, who referred to the condition as an “effeminacy of men.” Several medical and surgical treatments of gynecomastia were described in the 1800s.
Treatment of gynecomastia has continued to evolve over the ages. Presently, a multifaceted surgical approach is used to optimize correction of the deformity. The fatty component is removed with one or a combination of the variants of liposuction, while the glandular component requires direct excision. The skin is redraped over the underlying structures or, in severe cases, resected. The patient’s treatment plan should be crafted to correct the specific problems that are unique to his specific case.
What are the complications?

Risk factors for gynecomastia include:
- Adolescence
- Older age
- Use of anabolic steroids or androgens to enhance athletic performance
- Certain health conditions, including liver and kidney disease, thyroid disease, hormonally active tumors, and Klinefelter’s syndrome
Complications
Gynecomastia has few physical complications, but it can cause psychological or emotional problems caused by appearance.
What can you do to speed up recovery?
The recovery time required for Gynecomastia surgery is 4 to 6 weeks, obviously depending on the recovery pace and your health condition. Surgeons usually recommend the first two or three days of total rest so that the healing process does not get disrupted. Immediately after the surgery, you might face some uneasiness, pain, tightness or tenderness in the operated area. But gradually after a week or so, these will go away. You might have to visit your surgeon to remove the stitches after a week.
However, you have to follow the instructions as suggested by your surgeon to gain a healthy speedy recovery and to avoid complications.
- Diet- Immediately after the surgery the patients are recommended to take clear fluids and then gradually switching to solid diets. It has to be made sure that the patient takes a regular meal with plenty of water content in it. You can add fruit juice, soft drinks to prevent dehydration. Alcohol must be strictly prohibited for 72 hours before and after the surgery. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol.
- Activities- The more rest, the better will be your surgical recovery. In the first twenty-four hours post surgery, it is recommended for not doing any strenuous activity like driving or operating the heavy machinery. Later on from the second day, you must take brisk walks that can help you in quick recovery. You do not have to stay in the bed the whole time. On the second day or third, you can drive and engage yourself in moderate activities but never any strenuous activity like gym, aerobics, running or swimming. You have to keep increasing your daily activities day by day gradually without going beyond your tolerance level. However, people normally go back to their office after 2 or 3 days.
- Compression garment– During the recovery period the most highly recommended thing is wearing a compression garment. Wearing this will help reduce the swelling and bruising and will improve the aesthetic outcome. The compression garment is to be worn twenty-four hours for the first week post surgery. In the second week, reduce it to 18 hours a day. The cleanliness and hygiene of the compression garment must be maintained properly to avoid infection. Wash off the garment in cold water and dry it. After three weeks you can replace your compression garment with any comfortable wear.
- Be careful– You have to be very careful about taking already prescribed medicines. You are supposed to start them after two days or 48 hours of the surgery. You should also stop drinking alcohol and smoking before and after three days of the surgery. Activities like this will reduce the blood flow and start creating complications.
Finally, maintain a healthy and hygienic lifestyle and keep cleaning your incisions with clean water daily. Apply antibiotic ointments and cover them with a new dressing is required. Take care of yourself and be safe!
Do you need to rest up afterwards and for how many days?
During your gynecomastia surgery recovery period, dressings or bandages will be applied to your incisions and an elastic bandage or support garment may be used to minimize swelling and support your new chest contour as it heals after surgery.
A small, thin tube may be temporarily placed under the skin to drain any excess blood or fluid that may collect.
You will be given specific instructions that may include how to care for the surgical site and drains, medications to apply or take orally to aid healing and reduce the potential for infection, specific concerns to look for at the surgical site or in your general health and when to follow up with your plastic surgeon.
Be sure to ask your plastic surgeon specific questions about what you can expect during your individual recovery period.
- Where will I be taken after my surgery is complete?
- What medication will I be given or prescribed after surgery?
- Will I have dressings/bandages after surgery? When will they be removed?
- Are stitches removed? When?
- When can I resume normal activity and exercise?
- When do I return for follow-up care?
It’s very important to follow your plastic surgeon’s instructions and attend follow-up visits as scheduled.
The final results of gynecomastia surgery are permanent in many cases. However, if gynecomastia resulted from the use of certain prescription medications, drugs (including steroids) or weight gain you must be fully free from these substances and remain at a stable weight in order to maintain your results.
Before & After Gallery